What is Layer 0 Blockchain?
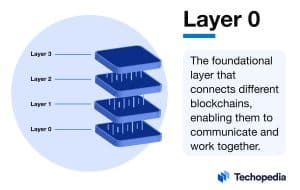
In the crypto space, Layer 0 acts as the foundational layer upon which other blockchains, particularly Layer 1 blockchains, are built. In simple Layer 0 definition, it can be considered the “blockchain for blockchains.”
Layer 1 blockchains, such as Ethereum and Solana, provide the foundational structure that developers use to build their applications. These chains are largely monolithic, where all features occur within one interdependent codebase.
As these networks gain popularity, they face the blockchain trilemma. This refers to the trade-off between 3 critical aspects of blockchain technology: security, scalability, and decentralization.
Layer 2 blockchains, on the other hand, are designed to enhance the capabilities of Layer 1 blockchains by providing scaling solutions. These solutions, such as the Lightning Network and Plasma, focus on improving network efficiency and increasing transaction throughput.
Layer 3 encompasses protocols built on top of Layer 2, providing application-specific networks. This includes various decentralized applications (dApps), crypto wallets, and blockchain-based games.
However, the monolithic nature of Layer 1 blockchains leads to congestion and inefficiencies. This is where Layer 0 steps in, aiming to address these issues by enhancing interoperability and scalability.
Key Takeaways
- Layer 0 is the foundational layer in the blockchain ecosystem.
- It addresses key issues like interoperability and scalability.
- Layer 0 protocols offer flexibility for developers, allowing for the creation of customized blockchains with specific functionalities.
- Technologies like parallel processing and sharding in Layer 0 improve the performance, speed, and cost-efficiency of blockchain operations.
- The adoption and success of Layer 0 protocols depend on overcoming complexity and security challenges while delivering real value to users and attracting developers.
How Layer 0 Works
Layer 0 functions as a bridge between the physical world and higher layers of the blockchain. These blockchains optimize data transfer between Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks, enhancing overall efficiency and scalability.
As the lowest layer in the blockchain stack, Layer 0 deals with the core infrastructure of the network. Its primary focus is on improving data transfer and communication between different blockchain layers, which in turn ensures smoother and faster operations.
What Problems Can Layer 0 Solve?
Layer 0 blockchains can tackle some of the most common issues in the blockchain space, including interoperability, scalability, and flexibility.
Interoperability
One of the main benefits of Layer 0 is its ability to facilitate interoperability between blockchains. In other words, blockchains built on the same Layer 0 protocol can interact seamlessly without the need for dedicated bridges.
This is specifically important as an interconnected ecosystem of blockchain-enabled products and services enhances the user experience, attracting more users. Moreover, this cross-chain interaction results in faster transaction speeds and greater efficiency.
Scalability
Blockchains like Ethereum often face congestion issues because they handle all their functions on a single Layer 1 protocol. Layer 0 aims to sidestep this tie-up by delegating these functions to different blockchains.
Using this design, each blockchain within the same Layer 0 infrastructure can optimize specific tasks, enhancing scalability. For instance, execution chains can be fine-tuned to handle high transaction volumes per second.
Developer Flexibility
Layer 0 protocols often provide user-friendly software development kits (SDKs) and interfaces, making it easier for developers to launch their own specialized blockchains.
These protocols offer great flexibility, allowing developers to customize their blockchains, define their own token issuance models, and control the type of dApps built on their networks.
Layer 0 vs. Layer 1 and Layer 2
Purpose: Facilitate interoperability and connectivity between different blockchains
Examples: Polkadot, Cosmos
Scalability: High, as it connects multiple blockchains, enabling parallel processing
Security: Provides a foundational security model but depends on the individual security of connected chains
Interoperability: Very high, primary function is to connect different blockchains
Consensus Mechanism: Consensus mechanisms vary and depend on the protocol
Transaction Speed: Potentially very high
Purpose: Ensure security, consensus, and the main transaction record
Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain
Scalability: Limited by the blockchain’s inherent capabilities (e.g., block size, consensus mechanisms)
Security: High, relies on consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) for security
Interoperability: Limited to its own ecosystem; cross-chain operations are typically difficult
Consensus Mechanism: Various mechanisms like PoW and PoS
Transaction Speed: Moderate to low, depending on network congestion and block time
Purpose: Enhance scalability, speed, and transaction throughput without compromising Layer 1 security
Examples: Lightning Network (Bitcoin), Optimistic Rollups (Ethereum)
Scalability: High, designed specifically to handle more transactions faster than Layer 1
Security: Relies on Layer 1 security but adds additional security protocols
Interoperability: Depends on Layer 1 for interoperability; can be designed to interact with multiple Layer 1 networks
Consensus Mechanism: Inherits consensus from Layer 1 but can have additional mechanisms for validation
Transaction Speed: High, designed to process transactions off-chain and settle on-chain later
Use Cases for Layer 0 Blockchains
Layer 0 chains have a number of use cases, which makes them a valuable innovation to look forward to.
For one, Layer 0 networks offer a highly customizable infrastructure for specialized blockchains. Networks like Avalanche and Solana provide developers with the flexibility to create bespoke networks tailored to specific requirements.
This includes customization of consensus mechanisms, transaction speeds, and interoperability features, making them ideal for applications requiring ultra-fast transaction processing, such as high-frequency trading in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Furthermore, Layer 0 networks support cross-chain communication, enabling seamless interactions between diverse blockchains. This is particularly useful for projects that bridge assets or data across different ecosystems.
Layer 0 Pros and Cons
Like any other invention, Layer 0 blockchains have their own unique benefits and disadvantages.
Pros
- Better performance and speed
- Improved privacy and security
- Cost reduction
Cons
- Complexity
- Adoption
- Security risks
Future for Layer 0 Protocols
Layer 0 protocols can evolve to become a crucial aspect of blockchain technology thanks to their core features, such as interoperability, scalability, and cross-chain functionality.
However, for these blockchains to gain widespread use, they need to address issues such as complexity and security. Furthermore, their ability to attract developers and deliver valuable applications to users will impact their adoption.
The Bottom Line
Layer 0, meaning the most basic layer in the blockchain hierarchy, offers solutions to some of the prominent challenges faced by earlier blockchain architectures. Its ability to enhance interoperability, scalability, and developer flexibility positions it as an important component in the growth and expansion of blockchain technology.