What is Automation?
Automation is the creation and use of technology to produce and deliver goods and services with minimal human intervention.
The implementation of automation technologies, techniques, and processes improves the efficiency, reliability, and/or speed of many tasks that were previously performed by humans.
Key Takeaways
- The goal of automation is to use technology to improve human productivity.
- Automation is a spectrum that includes simple task automation as well as complex AI-driven decision-making.
- Automated systems ensure consistent output and can improve the quality of products and services by minimizing human error.
- While automation can lead to job displacement in certain sectors, it also creates opportunities in others.
- Automated systems will always require human supervision.
History of Automation
The concept of automation predates the Industrial Revolution and can be traced back to ancient civilizations when simple machines like water wheels were used to automate the repetitive motions required to grind grain.
Today, automation encompasses a wide spectrum of technologies, from software bots that buy and sell currencies to hardware bots that automate production lines in manufacturing.
How Automation Works
Ultimately, automation relies on instructions or rules that tell the technology what to do. The instructions can be programmed into software, written in code, or even learned autonomously through artificial intelligence (AI).
The specifics of how automation works can vary depending on the context and the technology being used, but the underlying principle is to streamline tasks and reduce the need for human involvement as much as possible.
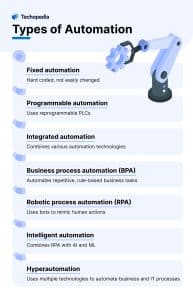
Types of Automation
Different types of automation can be categorized based on their complexity, application, and technology used.
Some common types include:
Why Use Automation
Automation can be expensive initially, but in the long term, it can minimize costs by reducing the need for manual labor.
Additionally, automation can improve productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by reducing human error and increasing the speed at which tasks are completed.
Automation Use Cases
Automation is present in virtually all vertical and niche industries today, including manufacturing, transportation, security, and finance.
For example, the best accounting software can automate a number of manual processes, including:
- Data entry and accounts payable
- Bank reconciliation
- Expense tracking
- Financial reporting
Automation not only saves accountant managers time and reduces errors, it also allows them to focus on higher-value activities.
Examples of Automation
Automation is playing an important role in many aspects of our daily lives. At home, smart thermostats can adjust temperature settings based on occupancy patterns, and robotic vacuum cleaners can autonomously navigate and clean floors.
Automation is even more pervasive in manufacturing and business:
Automation and Job Loss
Automation has historically been a double-edged sword in terms of employment and job loss.
On one hand, automation can enhance efficiency, reduce human error, and allow businesses to scale operations with greater precision.
On the other hand, automation can dramatically change the job market and underscore the need for reskilling and upskilling programs that help the workforce adapt to the changing job landscape.
Upskilling involves acquiring new skills or enhancing existing ones to remain relevant in a current job. Reskilling involves learning entirely new skills to transition into a different career path. Both strategies are important for adapting to the changing demands that increased automation is having on the job market.
The good news is that as businesses seek to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs, the need for skilled professionals who can design, implement, and manage automation solutions has grown significantly.
If you’re interested in a career in automation, acquiring skills in areas like programming, robotics, data analysis, and machine learning can open up a wide range of opportunities.
Automation Pros and Cons
While automation offers numerous benefits in terms of efficiency, labor cost savings, and safety, it also presents challenges related to initial costs and workforce optimization. Balancing these pros and cons is essential for effectively integrating automation into different business and industry sectors.
Pros
- Increased efficiency
- Cost reduction
- Consistency
- Provide data-driven insights
- Enable 24/7 operation
- Reduces the risk of injury to human workers
Cons
- Job displacement
- Create new types of security risks
- Initial investment can be high
- Creativity limits
- Loss of human connection
- Technical issues can create costly disruptions
The Bottom Line
Automation’s meaning has evolved over time. Initially, the concept involved using mechanical technology to complete manual tasks. Today, it includes intelligent systems that can make decisions on their own.
As AI and ML continue to advance, new types of automation will be designed to tackle increasingly complex tasks and challenges. You can expect that automation will continue to revolutionize industries, transform the workforce, and reshape the way we live and work as it has throughout history.