What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
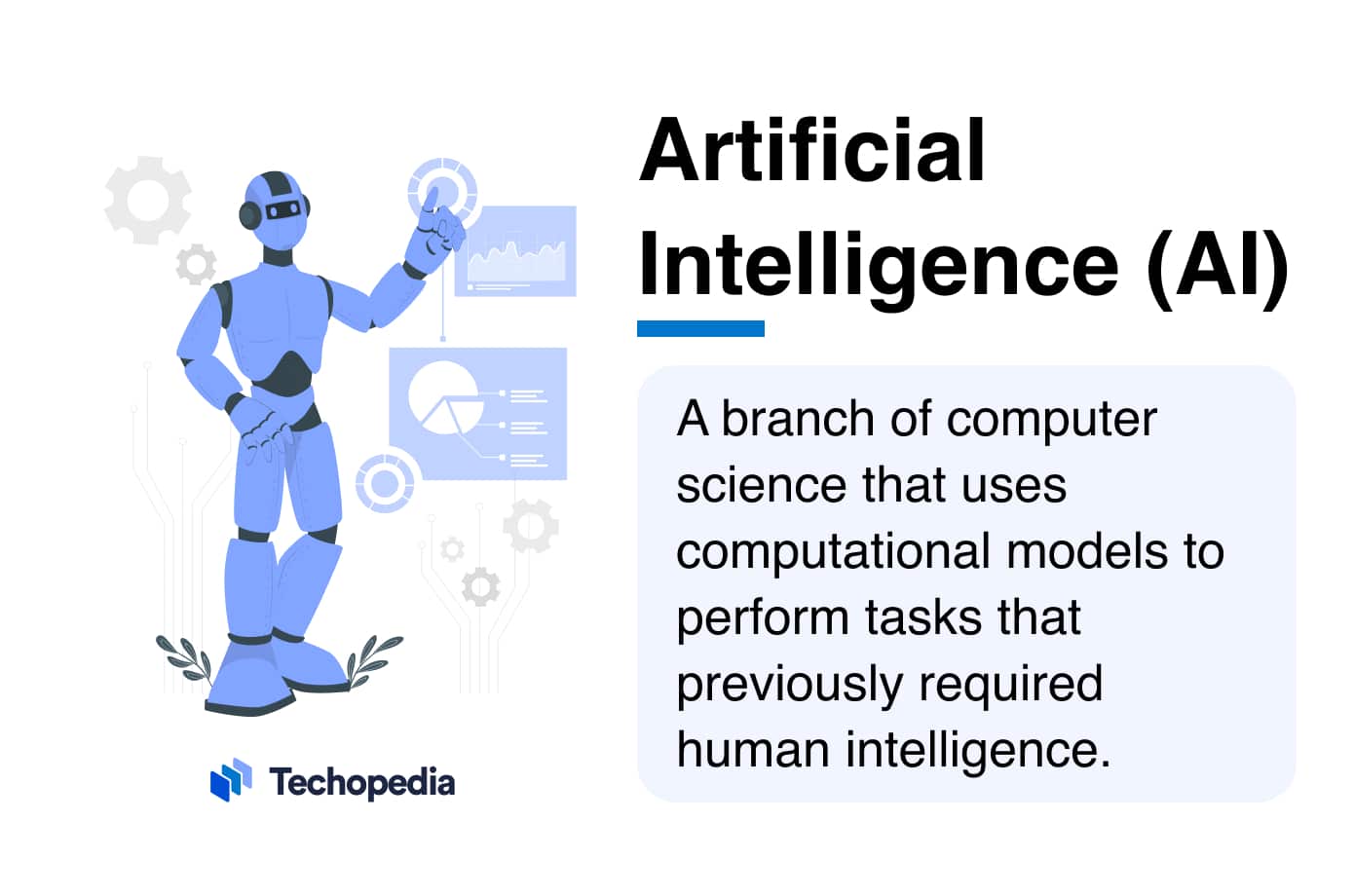
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the development, deployment, and maintenance of computational systems that can replicate certain types of human intelligence. Currently, this aspect of computer science is focused on creating algorithms and programming machine learning (ML) models that can analyze vast amounts of data to gain insights and make data-driven decisions autonomously.
Essentially, artificial intelligence initiatives combine elements of mathematics and computational neuroscience to simulate and/or enhance human thought processes. An important goal of this research field is to investigate how technology can be used to carry out cognitive tasks that humans find tedious or challenging.
AI is considered to be a disruptive technology because it is changing the way people access and process information, do their jobs, and understand the nature of creativity and originality.
Techopedia Explains the AI Meaning
Most AI definitions explain the positive aspects of using artificial intelligence to enhance human intelligence and help people be more productive.
It should be noted, however, that critics of the technology have expressed concerns that increasingly powerful AI models could soon surpass human intelligence and eventually become a threat to humanity.
The uncontrolled advancement of AI and the technology’s potential to accelerate beyond human control is sometimes referred to as The Singularity. The theoretical potential for The Singularity to become real is just one reason why governments, industry segments, and large corporations are putting AI guardrails in place to minimize risk and ensure that artificial intelligence is used responsibly.
How Artificial Intelligence Works
Today, AI applications typically use advanced machine learning algorithms and vast amounts of computational power to process, analyze, and learn from data in ways that mimic specific aspects of human cognition, like pattern recognition and inductive reasoning.
The first step when developing an AI model that uses ML involves data acquisition. The specific data type will be determined by the AI’s intended function. For example, an image recognition model will require a massive dataset of digital images.
Once the data has been collected, data scientists can select or develop algorithms to analyze the data. The algorithms – which are essentially sets of instructions – are sets of instructions that tell the computer how to process data and arrive at an output.
Many machine learning algorithms, including deep learning algorithms, are designed to be used iteratively. They get exposed to data, make predictions/decisions, and then receive feedback to adjust their internal processes. The process of allowing algorithms to improve their outputs over time is referred to as machine learning (ML).
The learning process can be supervised or unsupervised, depending on how the data is presented and what the AI programming is meant to achieve.
With supervised learning, the AI model learns from a dataset that includes both the input and the desired output. With unsupervised learning, the algorithm identifies patterns, relationships, or structures in the data it receives and then uses the analysis to predict outputs.
Once an AI model can reliably predict outputs for unseen training data with an acceptable range of accuracy, it can be tested with real-world data. At this point, the model will either be retrained or deployed and monitored continuously for model drift.
H3: The Difference between Machine Learning and AI
While AI and ML are often used as synonyms, the artificial intelligence meaning is an umbrella term, and machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence. Essentially, every ML application can be referred to as AI, but not all artificial intelligence applications use machine learning. For example, rule-based symbolic AI falls under the AI umbrella, but it isn’t a true example of machine learning because it doesn’t learn from data the way ML does.
Examples of AI Technology
Today’s AI often uses machine learning in conjunction with other computational techniques and technologies. A hybrid approach allows for more nuanced and robust AI systems.
For example, deep learning is an iterative approach to artificial intelligence that stacks machine learning algorithms in a hierarchy of increasing complexity and abstraction. It is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture in use.
Other well-known AI techniques and technologies include:
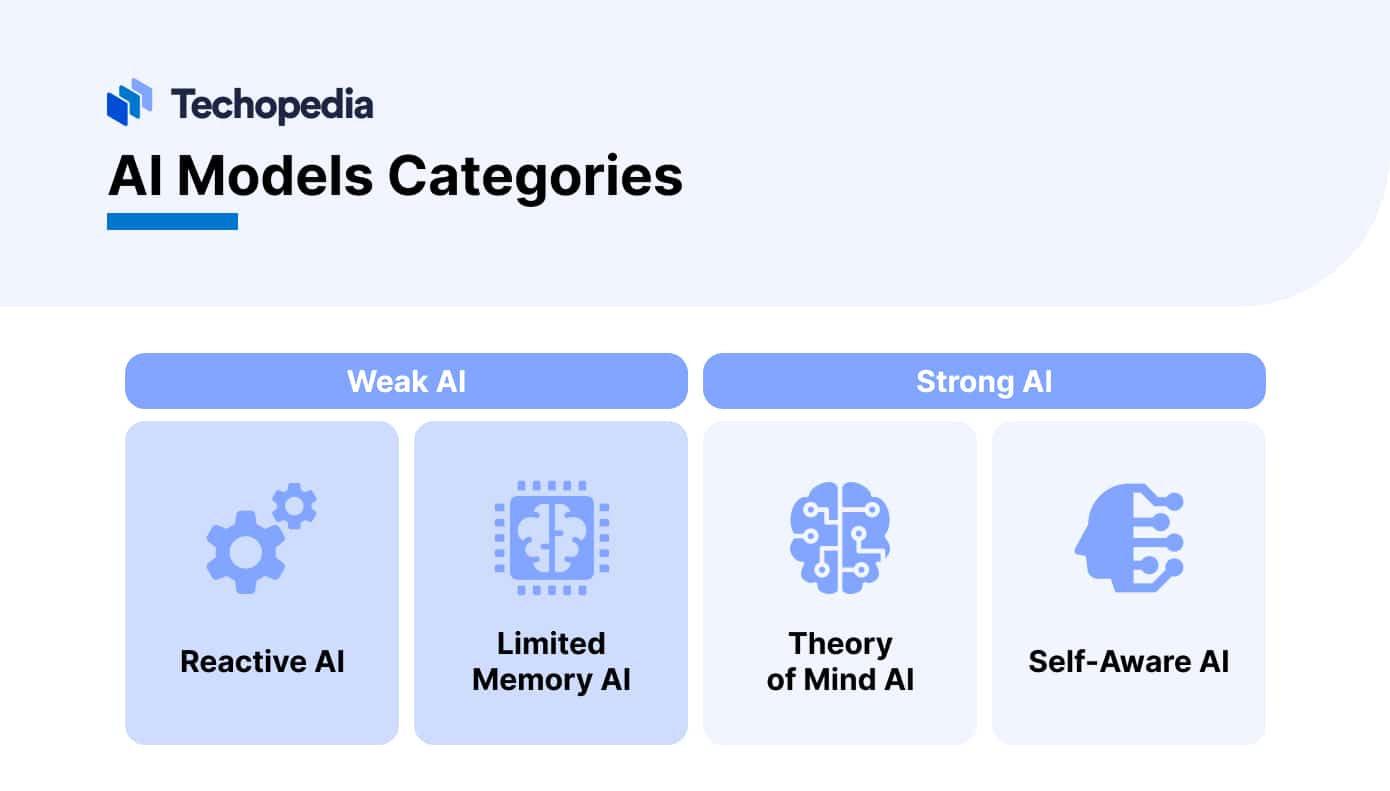
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can be categorized as being either weak AI or strong AI. All artificial intelligence in use today is considered to be weak AI.
Weak AI
Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is capable of performing a limited number of predetermined functions.
Even powerful multimodal AI chatbots like Google Gemini and ChatGPT are still a type of weak AI. These two families of large language models (LLMs) had to be programmed how to respond to user prompts, and they will require more programming if they are going to be used for new tasks.
Strong AI
Strong AI doesn’t exist yet, but researchers and AI advocates have expressed interest in two distinct types of strong AI: artificial general intelligence (AGI) and artificial superintelligence.
Artificial general intelligence is a hypothetical type of AI that possesses human-level intelligence. In theory, AGI will be able to learn, reason, and solve problems in an interdisciplinary manner across all domains. The technology will be able to respond autonomously to new types of outside stimuli without explicit programming.
Superintelligence is the type of hypothetical AI that is often depicted in science fiction books. This type of AI will far surpass AGI capabilities and be more intelligent than human beings.
It’s important to note that no AGI or superintelligent systems have been developed yet, and there is still considerable debate among experts about when – or even if – they will be achieved. The negative and positive implications of superintelligence are the subject of much debate within the AI community and society at large.
AI models can also be categorized by their decision-making capabilities and levels of cognitive sophistication.
AI Use Cases in Business
Artificial intelligence technology is streamlining business operations and increasing efficiency across various business sectors, but it is also requiring employees to upskill and adapt to new roles and responsibilities within the workplace.
As routine tasks become automated, the workforce is expected to shift towards more analytical, creative, and supervisory roles that AI technology cannot fulfill. The hope is that the transition will not only enhance employee productivity, it will also allow employees to focus on strategic and creative tasks that add greater value to the business.
The ability of AI to analyze vast amounts of data in real time is enabling businesses to tailor their offerings to specific customer segments and identify opportunities for growth and improvement more effectively than ever before. The integration of AI in business operations is also transforming marketing engagement strategies. Personalized recommendations and chatbots that provide interactive customer service 24/7 are allowing companies to offer unprecedented levels of customer support.
Benefits and Risks of Artificial Intelligence
As AI becomes a standard technology for business applications, there is growing concern about its ethical use, benefits, and risks.
The ethical use of AI calls for careful consideration and management of these risks to ensure that the technology is used in a way that is beneficial to society and does not exacerbate inequalities or harm individuals or groups.
Artificial intelligence has also introduced complex legal considerations that businesses must navigate carefully. These concerns include issues related to data privacy, AI bias and the impact of AI on employment, as well as its impact on society.
Determining who is responsible when AI systems make harmful decisions can be challenging, especially for complex AI systems whose outputs have hundreds or even thousands of dependencies. For example, when an AI-powered self-driving car causes an accident, determining who is liable – the developer, the company, or the user – is a significant challenge. It’s even more complicated if the vehicle’s operation has been compromised by a malware attack.
It’s becoming increasingly clear that companies need to establish clear guidelines and best practices to ensure that employee use of AI-enhanced technology remains in compliance with corporate policies.
The table below provides a high-level view of AI’s dual-edged nature.
Pros
- Efficiency & productivity gains
- Enhanced problem-solving
- Personalized experiences
- Innovation & breakthroughs
Cons
- Job displacement
- Algorithmic bias
- Privacy infringement
- Lack of transparency & accountability
Regulatory Compliance and Artificial Intelligence
As AI applications become more integrated into critical sectors of e-commerce, agriculture, healthcare and finance, the need for sharing best practices and adopting standardized AI frameworks like NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework and Google SAIF has never been greater.
To reduce the economic and societal risks of developing and/or using AI, many countries around the world are creating new policies, laws, and regulations.
Here is a short list of some of the initiatives currently in play:
The Bottom Line
The development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technology to automate tedious tasks and maximize personal and professional productivity will require industry standards and regulatory oversight that balances innovation with AI’s responsible use.
FAQs
What is artificial intelligence in simple terms?
What AI is used for?
What is an example of artificial intelligence?
Is AI good or bad?
References
- Top 5 Disruptive Technologies to Change the World (Professionalprograms.mit)
- The Rise and Fall of Symbolic AI (Towardsdatascience)
- Sequential Analysis of Statistical Data (Nature)
- Fact Sheet: Biden-Harris Administration Announces Key AI Actions Following President Biden’s Landmark Executive Order (Whitehouse)
- Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy (Ised-isde.canada)
- Sign in to your Microsoft account (D.docs.live)
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (Niti.gov)
- An Overview of the Regulation of AI in Japan (Linkedin)
- 과학기술정보통신부 (Msit.go)